Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) has introduced a generous incentive for lithium-ion energy storage that could reduce energy storage system installation costs by up to 2/3. This makes Japan the second country in the world–after Germany–to offer strong subsidies for energy storage as part of a drive to increase renewable energy uptake.
Energy storage systems to be included under the incentive will start as small as those with a capacity of 1 kilowatt-hour (kWh). Individuals who install a system will be eligible to receive up to the equivalent of about USD$10,000 for a system, while businesses may receive up to around USD$100,000. Systems must fulfill certain criteria to be eligible, including assessment and accreditation through the country’s Sustainable Open Innovation Initiative.
The reasons cited by METI for the introduction of the scheme include the need to address the energy problems that the country has faced since the Fukushima nuclear disaster 3 years ago. The Ministry hopes that greater uptake of energy storage will allow for better harvest of and use of the power produced by the country’s rapidly expanding solar PV system fleet.
This could in turn improve Japan’s energy independence by reducing the amount of fuel the country needs to import from abroad. There are also hopes that greater uptake of will result in downward pressure on lithium-ion battery technology prices. Lithium-ion batteries prices have dropped significantly in recent years.
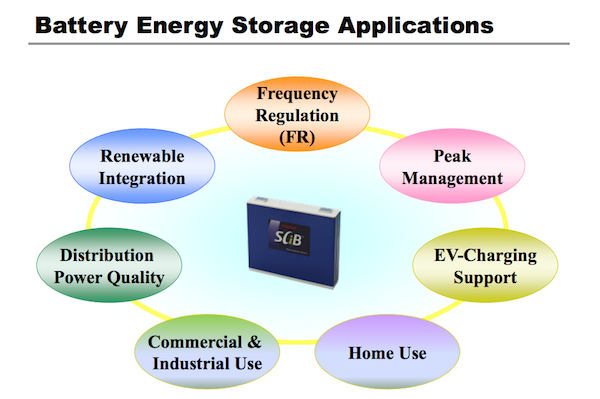
Energy storage promises a number of other benefits to electricity infrastructure. According to Toshiba, with regard to renewable energy integration, energy storage can suppress power fluctuation, manage & set aside surplus power, and enhance transmission capacity. Among the other more general benefits are frequency regulation, plus management of distribution power quality and reduction of peak electricity demand.
Image via Toshiba
METI has already backed 2 large-scale energy storage demo projects: One in Hokkaido which with a capacity of 15MW-60MWh and a 40MW-20MWh project in northeastern Japan. The Hokkaido project, once completed, will be the largest of its kind in the world.
Top image via Toshiba
© 2014 Solar Choice Pty Ltd